Assessment of Digestive System
- Nature of problem
- Major illnesses and hospitalization
- Medications
- Nutritional status
- Family history
- Social history
Physical Examination
- Height and weight
- Mouth and pharynx
- Inspect lips for symmetry, color, and presence of abnormalities
- Using penlight and tongue depressor, inspect the inner surfaces of the of the lips and oral mucosa
- Inspect teeth and gums
- Note significant mouth odors
- Assess pharynx and tonsils foe signs of inflammation, ulceration
- Ask the person to say ‘ah’
- Abdomen
General Principles
- Inspection, auscultation, percussion, palapation
- Proceed systematically from upper right quadrant moving clockwise
- Examine areas of pain and tenderness last
Preparing for examination
- Ask pt to empty bladder
- Have pt lie supine w/ knees slightly bent and arms at side
Inspection
- Skin – from neck to abdomen
- Architecture – symmetry of abdomen, shape,
- Movement - normal rise and fall during respiration (adults are not normally abdominal breathers), pulsations, peristaltis (not normally seen)
Auscultation
- Bowel sounds – normal: every 5-15 seconds, 5-35 per minute
- Circulatory sounds – pulsations, bruit
Percussion
- Determines the size and density of organs
- Percussion on abdomen is tympanic over air filled or dull in solid organs
Palpation
- Light palpation for masses and tendern
ess
- Deep palpation size and shape of organs and masses
- Rebound tenderness
Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests

Blood Level Assessments
- Amonia – elevation seen w/ liver disorders
- Amylase – elevated with pancreatitis
- Lipase – elevated during pancreatitis
- AST and ALT – elevated during liver disorders
- Urobilinogen – liver, gallbladder aor bile duct disorders

Urine and Stool Analysis
- Schilling’s test - test to determine perniciuos anemia
- Urine Urobilinogen- use to detect abnormality in bile excretion may be due to billary tract obstruction or inflammatory diseases of the liver and gallbladder
- Stool for occult blood: Hemoccult Guaiac Tests
- Usually 3 stools are collected and must reach laboratory w/n 6 hours
- For 3 days before the test:
- Avoid red meat in the diet
- Avoid foods with a high peroxidase, turnips, cauliflower, broccoli, radish, and melon.
- Avoid iron preparations, enemas and laxatives
- Analyze stool for fecal fat
- May be a random stool or pt may adhere to 3-day high fat diet followed by 72-hour collection of stool
- Culture
- Detect presence of bacteria, ova, or parasites
- Obtain freshly passed specimen and transport immediately to the laboratory
Gastric Analysis
- Measures the stomach’s secretion of hydrochloric acid and pepsin
- NPO for 12 hrs before the test
- NGT is inserted and residual contents are discarded
- During analysis, NGT is hooked to suction and contents are collected every 15 mins interval for 1 hour
- Increase levels may indicate ulcers
- Decrease levels may indicate carcinoma
- Radiologic test
- Upper Gastrointestinal Series and Small-Bowel Series
- used to detect esophageal disorders, gastric ulcers, tumors and small bowel disorders
- Explain procedure to patient.
- Clear liquid dinner, the night before the procedure. NPO after midnight. Narcotics and anticholinergics to be held 24 hours.
- pt drinks mixture of barium sulphate. Traces after 30 minutes. Small bowel are taken every 30 mins for 2-6 hours
-post procedure: laxative is given. Stool will be light in color for the next 2 to 3 days from the barium. Notify health care provider if he or she has not passed the barium in 2 to 3 days
- Water-soluble iodinated contrast agent (such as Gastrografin) may be used for a patient suspected perforation
- Barium Enema
- Purpose: visualization of the large intestine to detect masses, structure, inflammation
- Preparation: pt on clear liquid diet for 24 hours and NPO after midnight. Laxative or enema is given evening before the test
- Procedure: barium mixture is inserted through a rectal catheter. Air may be introduced after the barium. Patient is placed on various position and instructed to hold the enema. Test usually take 1 hour.
- Follow- up: laxative is ordered.
- Ultrasonography (ultrasound)
- Purpose: noninvasive and uses high frequency sound waves to image soft tissues and organs. Doppler may be used for vascular assessment
- Preparation: maintain NPO for 8-12 hours. If indicated, use laxative or enema.
- Procedure: a lubricated microphone transducer is placed on the abdomen and rubbed over the skin. There is no follow-up.
- Computed Tomography
- visualizes differences in tissue densities thus detects tumors and masses. x-ray technique that provides excellent anatomic definition
- NPO for 8-12 hours. Ask the patient if she a pregnant. If yes do not proceed with scan and notify health care provider. Ask if there are known allergies to iodine or contrast media.
- intravenous contrast media may be given to enhance imaging. Report symptoms of itching or shortness of breath. Pt is placed on a radiograph table and moved inside the scanning machine that emits loud clicking sounds as it moves to different positions. No follow-up.
- Endoscopic Procedures
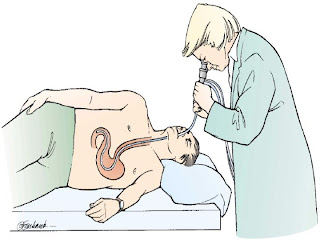
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
- Uses flexible endoscope to provide direct visualization of upper GIT
- client is placed on NPO for 4-6 hours. Medications such as atropine to lessen secretions and IV sedative may be given. Topical anethetics applied to the throat to depress gag reflex. Remove dentures.
- client is positioned on left side. lubricated endoscope passes down to GIT, pt is asked to swallow. Monitor V/S and airway. Air is inserted, pt may feel bloated.
-post procedure put client on NPO until gag reflex returns. May experience sore throat. Monitor for complications.
- Colonoscopy and Proctosigmoidoscopy
-uses flexible endoscope to provide direct visualization of large intestine, sigmoid and rectum
- pt is on clear liquid diet 24 hours before the test.
- IV sedative may be given to help the client relax.
- to remove feces and better visualization, laxative or enema are given.
- client is positioned on left side. lubricated endoscope passes through the anus, pt is asked to deep breath. Monitor V/S. Air may be inserted.
- after the procedure monitor V/S. Monitor for complications such as bleeding.






No comments:
Post a Comment